Welcome to the world of Estella Elisheva
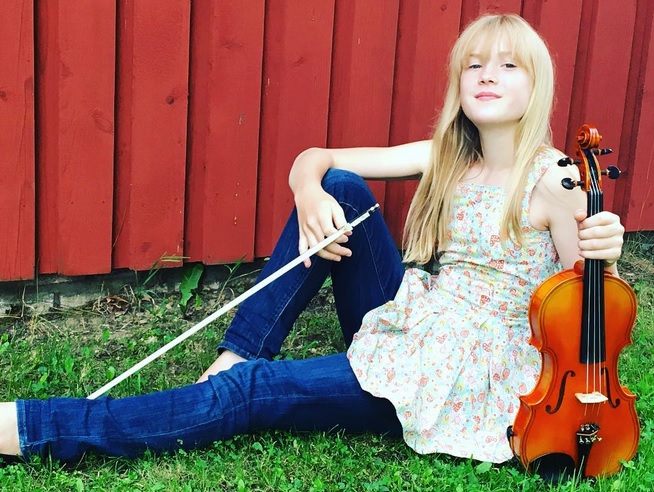

Practicing violin: Playing Opera Carmen “Habanera”
A post shared by Estella Elisheva (@estella.elisheva) on
Carmen (French pronunciation: [kaʁmɛn]; Spanish: [ˈkaɾmen]) is an opera in four acts by French composer Georges Bizet. The libretto was written by Henri Meilhac and Ludovic Halévy, based on a novella of the same title by Prosper Mérimée. The opera was first performed by the Opéra-Comique in Paris on 3 March 1875, where its breaking of conventions shocked and scandalized its first audiences.
Bizet died suddenly after the 33rd performance, unaware that the work would achieve international acclaim within the following ten years. Carmen has since become one of the most popular and frequently performed operas in the classical canon; the “Habanera” from act 1 and the “Toreador Song” from act 2 are among the best known of all operatic arias.
The opera is written in the genre of opéra comique with musical numbers separated by dialogue. It is set in southern Spain and tells the story of the downfall of Don José, a naïve soldier who is seduced by the wiles of the fiery gypsy Carmen. José abandons his childhood sweetheart and deserts from his military duties, yet loses Carmen’s love to the glamorous matador Escamillo, after which José kills her in a jealous rage. The depictions of proletarian life, immorality, and lawlessness, and the tragic death of the main character on stage, broke new ground in French opera and were highly controversial.
After the premiere, most reviews were critical, and the French public was generally indifferent. Carmen initially gained its reputation through a series of productions outside France, and was not revived in Paris until 1883. Thereafter, it rapidly acquired popularity at home and abroad. Later commentators have asserted that Carmen forms the bridge between the tradition of opéra comique and the realism or verismo that characterised late 19th-century Italian opera.
The music of Carmen has since been widely acclaimed for brilliance of melody, harmony, atmosphere, and orchestration, and for the skill with which Bizet musically represented the emotions and suffering of his characters. After the composer’s death, the score was subject to significant amendment, including the introduction of recitative in place of the original dialogue; there is no standard edition of the opera, and different views exist as to what versions best express Bizet’s intentions. The opera has been recorded many times since the first acoustical recording in 1908, and the story has been the subject of many screen and stage adaptations.
Background
In the Paris of the 1860s, despite being a Prix de Rome laureate, Bizet struggled to get his stage works performed. The capital’s two main state-funded opera houses—the Opéra and the Opéra-Comique—followed conservative repertoires that restricted opportunities for young native talent. Bizet’s professional relationship with Léon Carvalho, manager of the independent Théâtre Lyrique company, enabled him to bring to the stage two full-scale operas, Les pêcheurs de perles (1863) and La jolie fille de Perth (1867), but neither enjoyed much public success.
When artistic life in Paris resumed after the Franco-Prussian War of 1870–71, Bizet found wider opportunities for the performance of his works; his one-act opera Djamileh opened at the Opéra-Comique in May 1872. Although this failed and was withdrawn after 11 performances, it led to a further commission from the theatre, this time for a full-length opera for which Henri Meilhac and Ludovic Halévy would provide the libretto. Halévy, who had written the text for Bizet’s student opera Le docteur Miracle (1856), was a cousin of Bizet’s wife, Geneviève; he and Meilhac had a solid reputation as the librettists of many of Jacques Offenbach’s operettas.
Bizet was delighted with the Opéra-Comique commission, and expressed to his friend Edmund Galabert his satisfaction in “the absolute certainty of having found my path”. The subject of the projected work was a matter of discussion between composer, librettists and the Opéra-Comique management; Adolphe de Leuven, on behalf of the theatre, made several suggestions that were politely rejected. It was Bizet who first proposed an adaptation of Prosper Mérimée’s novella Carmen. Mérimée’s story is a blend of travelogue and adventure yarn, possibly inspired by the writer’s lengthy travels in Spain in 1830, and had originally been published in 1845 in the journal Revue des deux Mondes. It may have been influenced in part by Alexander Pushkin’s 1824 poem “The Gypsies”, a work Mérimée had translated into French; it has also been suggested that the story was developed from an incident told to Mérimée by his friend the Countess Montijo. Bizet may first have encountered the story during his Rome sojourn of 1858–60, since his journals record Mérimée as one of the writers whose works he absorbed in those years.
Georges Bizet (French: [ʒɔʁʒ bizɛ]; 25 October 1838 – 3 June 1875), registered at birth as Alexandre César Léopold Bizet, was a French composer of the romantic era. Best known for his operas in a career cut short by his early death, Bizet achieved few successes before his final work, Carmen, which has become one of the most popular and frequently performed works in the entire opera repertoire.
During a brilliant student career at the Conservatoire de Paris, Bizet won many prizes, including the prestigious Prix de Rome in 1857. He was recognised as an outstanding pianist, though he chose not to capitalise on this skill and rarely performed in public. Returning to Paris after almost three years in Italy, he found that the main Parisian opera theatres preferred the established classical repertoire to the works of newcomers. His keyboard and orchestral compositions were likewise largely ignored; as a result, his career stalled, and he earned his living mainly by arranging and transcribing the music of others. Restless for success, he began many theatrical projects during the 1860s, most of which were abandoned. Neither of his two operas that reached the stage in this time—Les pêcheurs de perles and La jolie fille de Perth—were immediately successful.
After the Franco-Prussian War of 1870–1871, during which Bizet served in the National Guard, he had little success with his one-act opera Djamileh, though an orchestral suite derived from his incidental music to Alphonse Daudet’s play L’Arlésienne was instantly popular. The production of Bizet’s final opera, Carmen, was delayed because of fears that its themes of betrayal and murder would offend audiences. After its premiere on 3 March 1875, Bizet was convinced that the work was a failure; he died of a heart attack three months later, unaware that it would prove a spectacular and enduring success.
Bizet’s marriage to Geneviève Halévy was intermittently happy and produced one son. After his death, his work, apart from Carmen, was generally neglected. Manuscripts were given away or lost, and published versions of his works were frequently revised and adapted by other hands. He founded no school and had no obvious disciples or successors. After years of neglect, his works began to be performed more frequently in the 20th century. Later commentators have acclaimed him as a composer of brilliance and originality whose premature death was a significant loss to French musical theatre.
Family background and childhood
Georges Bizet was born in Paris on 25 October 1838. He was registered as Alexandre César Léopold, but baptised as “Georges” on 16 March 1840, and was known by this name for the rest of his life. His father, Adolphe Bizet, had been a hairdresser and wigmaker before becoming a singing teacher despite his lack of formal training. He also composed a few works, including at least one published song. In 1837 Adolphe married Aimée Delsarte, against the wishes of her family who considered him a poor prospect; the Delsartes, though impoverished, were a cultured and highly musical family. Aimée was an accomplished pianist, while her brother François Delsarte was a distinguished singer and teacher who performed at the courts of both Louis Philippe and Napoleon III. François Delsarte’s wife Rosine, a musical prodigy, had been an assistant professor of solfège at the Conservatoire de Paris at the age of 13. At least one author has alleged that his mother was from a Jewish family but this is not substantiated in any of his official biographies.
Georges, an only child, showed early aptitude for music and quickly picked up the basics of musical notation from his mother, who probably gave him his first piano lessons. By listening at the door of the room where Adolphe conducted his classes, Georges learned to sing difficult songs accurately from memory and developed an ability to identify and analyse complex chordal structures. This precocity convinced his ambitious parents that he was ready to begin studying at the Conservatoire even though he was still only nine years old (the minimum entry age was 10). Georges was interviewed by Joseph Meifred, the horn virtuoso who was a member of the Conservatoire’s Committee of Studies. Meifred was so struck by the boy’s demonstration of his skills that he waived the age rule and offered to take him as soon as a place became available.